Run a dbt Cloud job on pull request
If your git provider has a native integration with dbt Cloud, you can take advantage of the setup instructions here. This section is only for those projects that connect to their git repository using an SSH key.
If your git provider is not one with a native integration with dbt Cloud, but you still want to take advantage of CI builds, you've come to the right spot! With just a bit of work it's possible to setup a job that will run a dbt Cloud job when a pull request (PR) is created.
The setup for this pipeline will use the same steps as the prior page. Before moving on, follow steps 1-5 from the prior page
6. Create a pipeline job that runs when PRs are created
- Bitbucket
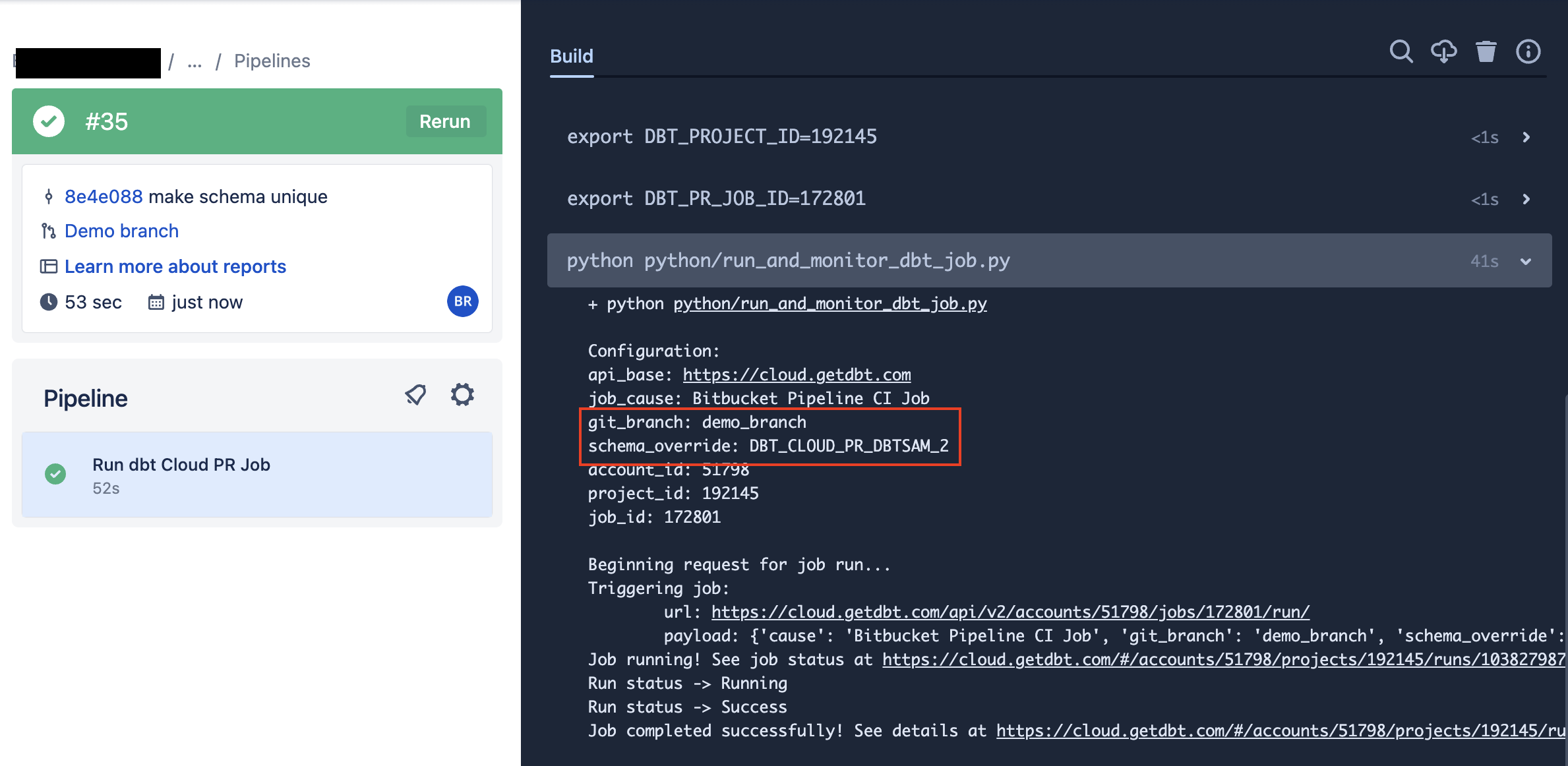
For this job, we'll set it up using the bitbucket-pipelines.yml file as in the prior step. The YAML file will look pretty similar to our earlier job, but we’ll pass in the required variables to the Python script using export statements. Update this section to match your setup based on the comments in the file.
What is this pipeline going to do?
The setup below will trigger a dbt Cloud job to run every time a PR is opened in this repository. It will also run a fresh version of the pipeline for every commit that is made on the PR until it is merged.
For example: If you open a PR, it will run the pipeline. If you then decide additional changes are needed, and commit/push to the PR branch, a new pipeline will run with the updated code.
The following varibles control this job:
DBT_JOB_BRANCH: Tells the dbt Cloud job to run the code in the branch that created this PRDBT_JOB_SCHEMA_OVERRIDE: Tells the dbt Cloud job to run this into a custom target schema- The format of this will look like:
DBT_CLOUD_PR_{REPO_KEY}_{PR_NUMBER}
- The format of this will look like:
image: python:3.11.1
pipelines:
# This job will run when pull requests are created in the repository
pull-requests:
'**':
- step:
name: 'Run dbt Cloud PR Job'
script:
# Check to only build if PR destination is master (or other branch).
# Comment or remove line below if you want to run on all PR's regardless of destination branch.
- if [ "${BITBUCKET_PR_DESTINATION_BRANCH}" != "main" ]; then printf 'PR Destination is not master, exiting.'; exit; fi
- export DBT_URL="https://cloud.getdbt.com"
- export DBT_JOB_CAUSE="Bitbucket Pipeline CI Job"
- export DBT_JOB_BRANCH=$BITBUCKET_BRANCH
- export DBT_JOB_SCHEMA_OVERRIDE="DBT_CLOUD_PR_"$BITBUCKET_PROJECT_KEY"_"$BITBUCKET_PR_ID
- export DBT_ACCOUNT_ID=00000 # enter your account id here
- export DBT_PROJECT_ID=00000 # enter your project id here
- export DBT_PR_JOB_ID=00000 # enter your job id here
- python python/run_and_monitor_dbt_job.py
7. Confirm the pipeline runs
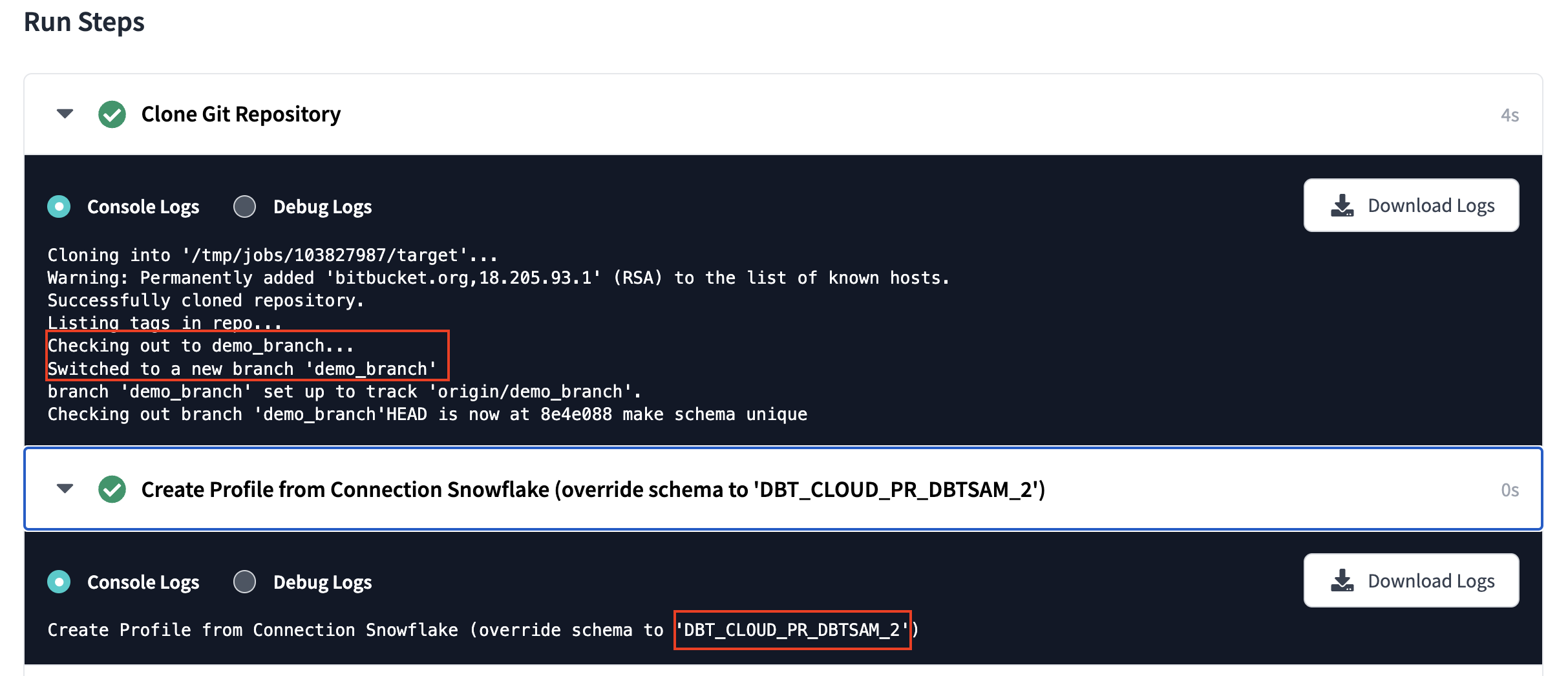
Now that you have a new pipeline, it's time to run it and make sure it works. Since this only triggers when a PR is created, you'll need to create a new PR on a branch that contains the code above. Once you do that, you should see a pipeline that looks like this:
- Bitbucket
Bitbucket pipeline:
dbt Cloud job:
8. Handle those extra schemas in your database
As noted above, when the PR job runs it will create a new schema based on the PR. To avoid having your database overwhelmed with PR schemas, consider adding a "cleanup" job to your dbt Cloud account. This job can run on a scheduled basis to cleanup any PR schemas that haven't been updated/used recently.
Add this as a macro to your project. It takes 2 arguments that lets you control which schema get dropped:
age_in_days: The number of days since the schema was last altered before it should be dropped (default 10 days)database_to_clean: The name of the database to remove schemas from
{#
This macro finds PR schemas older than a set date and drops them
The macro defaults to 10 days old, but can be configured with the input argument age_in_days
Sample usage with different date:
dbt run-operation pr_schema_cleanup --args "{'database_to_clean': 'analytics','age_in_days':'15'}"
#}
{% macro pr_schema_cleanup(database_to_clean, age_in_days=10) %}
{% set find_old_schemas %}
select
'drop schema {{ database_to_clean }}.'||schema_name||';'
from {{ database_to_clean }}.information_schema.schemata
where
catalog_name = '{{ database_to_clean | upper }}'
and schema_name ilike 'DBT_CLOUD_PR%'
and last_altered <= (current_date() - interval '{{ age_in_days }} days')
{% endset %}
{% if execute %}
{{ log('Schema drop statements:' ,True) }}
{% set schema_drop_list = run_query(find_old_schemas).columns[0].values() %}
{% for schema_to_drop in schema_drop_list %}
{% do run_query(schema_to_drop) %}
{{ log(schema_to_drop ,True) }}
{% endfor %}
{% endif %}
{% endmacro %}
This macro goes into a dbt Cloud job that is run on a schedule. The command will look like this (text below for copy/paste):

dbt run-operation pr_schema_cleanup --args "{ 'database_to_clean': 'development','age_in_days':15}"